S280 Science Matters
Summaries:
"The Rise and Fall of Leaded Petrol"
"Agriculture"
"Nuclear Power"
"Genetic Engineering"
"Changing Climate"
"Insulin: Discovery and Development"
Ex-S103ers Egg Yolk Survey!
S280 Course Description
New Scientist
Scientific American
ScienceNet
Nature: International Weekly Journal of Science
Climate Care
UK Climate Impacts Programme
Climate Change
Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research
Greenpeace version of "The day after tomorrow"
Online Biology Book
Embryology
DNA animations
DOE Genomes.org
ATP Synthesis
Lateral Science
Ghost Town (outside of Chernobyl)
Back to OU
TMA Scores
TMA01 71%
TMA02 88%
TMA03 67%
TMA04 0% (didn't do it!)
| Exam: 22nd October 2004 at 10:00-13:00 |
15th December 2005
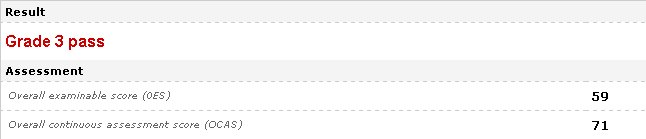
Today, at last - we got our results!
This'll do nicely, thank you! :)
2nd November 2004
Very late in updating this webpage after the exam - but have been shell-shocked!! AGAIN (as with S269) they asked all the wrong questions! Oh well - it's over at least!
22nd December 2003
We have mailing! The first 3 books etc + the first couple TMAs. I've listed the book contents below - and more on progress etc will appeara on the diary page.
15th December 2003
I registered for this course on Sunday (14th). It's the replacement for S365, Evolution, which I have withdrawn from. Hopefully, this one will be more interesting/do-able! I'm looking forward to it! The materials were despatched, to already registered students, last week - so hopefully should get those soon.
Book 1 THE RISE AND FALL OF LEADED PETROL introduces the aims and philosophy of the course, discussing how it complements courses that stress more theoretical aspects of science. This course emphasizes the way science impinges upon the world we live in, a point immediately illustrated by a case study on the scientific and social issues to do with the use of lead in petrol. This topic was selected for Book 1 because, unlike those dealt with in succeeding books, it has largely run its course and so can be looked at in the round, from the decision to add lead components to petrol to improve engine performance to the decision to eliminate lead from petrol for health reasons.
Contents
Two faces of science
Skills in Science Matters
Choosing an introductory topic
Introducing The Rise and Fall of Leaded Petrol
Lead: its chemistry, toxicity and measurement
Reactions of lead and some lead components
Lead poisoning
The measurement of lead
Lead in people
Lead levels in air
Lead levels in tap-water
Handling and interconverting units
Lead and Petrol
The motor car and the petrol engine
Engine knock and octane number
Making petrol
Lead in petrol: the options
Generating concern about leaded petrol: the scientific foundations
The safety margin in blood lead concentrations
The accumulation of lead in the global environment
Lead, child behaviour and child intelligence
The contribution of leaded petrol to a person's lead uptake
Vehicle exhaust emissions and the catalytic converter
Generating concern about leaded petrol: the political campaign
The beginnings
The WOPLIP report
The Lawther report
The environmentalists regroup
Conclusion
Reverberations
BOOK 2 AGRICULTURE looks at some of the ways science bears upon selected aspects of agriculture, including the spread of oilseed rape, the use of pesticides, animal production systems, BSE ('mad cow disease'), nitrate pollution and integrated farming systems.
Contents
Oilseed rape
Introduction
The erucic acid of rapeseed oil
The toxic glucosinolates of rapeseed meal
Eggs and Bacon
Introduction
Egg yolk colour
Environmental influences on egg production
Nutrient provision in pig production
Qualitative aspects of pig-meal
The 'nitrate problem'
'I only want my rights"'
Why owrry about nitrate in water?
Where does nitrate come from?
Who controls nitrate on the farm?
What really happens to nitrogen fertilizer?
The Nitrate Sensitive Areas schemes
Who else contributes to the nitrate problem?
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
Introduction
Cattle farming systems
Investigating the disease
What is the agent that causes BSE?
The risk of transmission of BSE to humans
Pesticides
Introduction
The discovery and development of pesticides
The contents of the poison cupboard
Application of pesticides
The fate of pesticides
Integrated farming systems
Introduction
Economic and political change
Integrated farming techniques
An integrated farming systems approach
Future developments
BOOK 3 NUCLEAR POWERbegins by presenting the scientific background to all aspects of nuclear power production, then considers the issues that arise from its use, including the risks, the economics, the disposal of radioactive waste and the proliferation of nuclear weapons.
Contents
Introduction and aims
Introduction
What are the aims of this book?
Nuclear power: the scientific background
Atoms and nuclei
Nuclear decay - radioactivity
Interactions between neutrons and nuclei
The dependence of nuclear reaction probabilities in uranium on neutron energy
The chain reaction and criticality
The production of fissile isotopes
Nuclear power: the technology
The components of a nuclear power station
Nuclear power reactor systems
Fuel requirements for nuclear reactors
Fast-breeder reactor systems
The biological effects of radiation
Introduction
Radiation damage to biological systems
Units of radiation dose
The health effects of radiation damage
Assessing the evidence for determining radiation exposure limits
Setting radiation dose limits
Leukaemia causes and clustering
The nuclear fule cycle
Mining uranium
Production of nuclear fuel
Radioactive discharges during normal reactor operation
The spent fuel
Fuel reprocessing
Strategies for dealing with high-level nuclear waste
High-level waste disposal
The opposition to nuclear waste disposal
Reactor accidents and risks
Radioisotopes and reactor accidents
The Windscale reactor accident
The accident at Three Mile Island
The Chernobyl accident
Risk assessment for reactor accidents
The Rasmussen Report
The economics of nuclear power
Energy and politics
Estimating hte costs of future projects
Cash flows in long-term projects
Research and development costs of nuclear power
The comparative costs of nuclear and fossil-fuelled power stations
Different views on the costs of nuclear power
A concluding activity
Nuclear weapons proliferation
The principles of nuclear weaponry
Production of fissile isotopes
The 'weapons connection' with nuclear power
The control of nuclear weapons proliferation
Energy and the future
Energy from fusion
Renewable energy sources
The UK energy scene and electricity production
In conclusion
Book 4 Genetic engineering considers the techniques that are now available to manipulate the genetic material of living organisms directly, and their use in medicine and in animal and plant breeding. What opportunities and threats does genetic engineering present? (This topic has been updated with a new supplement.)
Genetic engineering - media hype or real revolution?
Genetic engineering - why the interest?
Engineering new animals and plants
Novel microbial factories
A long history of exploitation
More microbes, more uses
Breeding better 'bugs'
Enter genetic engineering
Transferring genes into bacteria
The genes of E. coli
The essential steps in gene transfer into bacteria
Chopping up foreign DNA
Splicing in the genes
Getting the recombinant plasmids into bacteria
Getting the right gene product
Expressing genes
The problem of split genes
Workikng in reverse - how to by-pass introns
Getting the right clone
How many clones must we screen?
The microbial haystack - how to find a needle
Screening the gene product
Screening for genes directly
From shotgun to rifle
From bacteria to other cells
Putting phage to work
Other host cells
How to get the genes in and expressed
From single cells to whole multicellular organisms
Genetic engineering of plants and animals
Plant regeneration
The first genetic engineer?
Vectors and Ti plasmids
Cereal problems
Genetically engineered animals
Transgenic plants and animals - where now?
From laboratory to market-place
Medical applications of genetic engineering
The pharmaceutical industry
Diagnosis
Therapeutics
Cystic fibrosis
Agricultural applications of genetic engineering
Feeding the world
Targets in plant breeding
Rice
Wheat
Cotton
Targets in animal breeding
Improving farm animals
Pharming
The BST controversy
Epilogue: predicting the future
(Supplement)
Current uses of genetic engineering Gene and protein factories
Vaccines
Biological pest control
Use of viruses to introduce genes into cells
Improvement of commercially grown plants and animals
Organs for transplantation into humans
Experimental animals
Treatments for human genetic diseases
Transferring genes into bacteria
Amplifying DNA: the polymerase chain reaction.
From bacteria to other cells
Genetic engineering of plants and animals
Chimeras
Cloning
Medical applications of genetic engineering
The Human Genome Project
Gene therapy
Production of organs for transplantation
Agricultural applications of genetic engineering
Genetically modified crops: update
Development of resistant strains of insects
Harm caused to wildlife by B.t. crops
Gene tranfer into wild plants
Competition with wild plants
Cost effectiveness
Antisense technology: tastier tomatoes
Antibiotic resistance
Terminator seeds
Book 5 Changing climate is about the central question of global warming and climate change. Why is there so much controversy and uncertainty about future climate change? Can we turn to science for an answer?
Climate now: the Earth's climate system
The global energy balance
A wider look at the climate system
Linking the climate system together
Causes of climatic change
Past changes in climate
Lithospheric plate movements
Variations in the Earth's orbit
Variations in the solar constant
Volcanic activity
Atmospheric composition
The changing atmosphere
Carbon dioxide and the global carbon cycle
Other greenhouse gases: natural and unnatural
Drawing the threads together: what of the future?
Simulating climatic change
The 'radiative forcing' of climate
Modelling the climate system
Model validation
Equilibrium climatic change scenarios
Assessing the p[ace of climatic change
The 'detection issue'
The issue
Global warming trends: the instrumental record
The question of attribution
The 'climate debate' of the late 1980s
Future climates: projections and scenarios
Emission scenarios
What might a 'Business as Usual' future be like?
What about surprises?
Potential impacts of climatic change
Changes in sea-level
Effects on living organisms
Impacts on natural communities and agriculture
Economic and political impacts
Responding to the challenge
Response strategies
The Framework Convention on Climate Change
Science and the international review process
Negotiating limits
Book 6 Insulin: discovery and development looks at the controversial events surrounding the discovery of insulin, at how this important hormone is used nowadays to control diabetes, and at what medical innovations may lie ahead.
Discovery
The biological background
The moments of discovery
Development
Changes of attitude and increased understanding
New technology for old
New insulins for old
The search for a cure
Looking ahead: future promise
Book 7 Discovering the deep oceans looks at some of the revolutions in thought that had to occur before we could even begin to understand how the oceans work.
Clear, still and heavier than molten gold
The azoic theory
The 4-degree fallacy
The launch of the Challenger Expedition
From lifeless abyss to cradle of creation
The continuity of the chalk
The strange story of Bathybius
'Bathysnap' and beyond
An alterative way of life
A FAMOUS adventure
Getting warmer ...
Whales as stepping-stones
Postscript
The Open University Home Page
OU Student Home Page